Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji; Koike, Katsuaki*
Mathematical Geosciences, 56(2), p.333 - 360, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)To enable proper remediation of accidental groundwater contamination, the contaminant plume evolution needs to be accurately estimated. In the estimation, uncertainties in both the contaminant source and hydrogeological structure should be considered, especially the temporal release history and hydraulic transmissivity. Although the release history can be estimated using geostatistical approaches, previous studies use the deterministic hydraulic property field. Geostatistical approaches can also effectively estimate an unknown heterogeneous transmissivity field via the joint data use, such as a combination of hydraulic head and tracer data. However, tracer tests implemented over a contaminated area necessarily disturb the in situ condition of the contamination. Conversely, measurements of the transient concentration data over an area are possible and can preserve the conditions. Accordingly, this study develops a geostatistical method for the joint clarification of contaminant plume and transmissivity distributions using both head and contaminant concentration data. The applicability and effectiveness of the proposed method are demonstrated through two numerical experiments assuming a two-dimensional heterogenous confined aquifer. The use of contaminant concentration data is key to accurate estimation of the transmissivity. The accuracy of the proposed method using both head and concentration data was verified achieving a high linear correlation coefficient of 0.97 between the true and estimated concentrations for both experiments, which was 0.67 or more than the results using only the head data. Furthermore, the uncertainty of the contaminant plume evolution was successfully evaluated by considering the uncertainties of both the initial plume and the transmissivity distributions, based on their conditional realizations.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/07
The stress intensity factor (SIF) for crack at nozzle corner is a key parameter in structural integrity assessment of nozzle in reactor pressure vessel (RPV). Although various SIF solutions for surface cracks at nozzle corners have been proposed, most of them are only focusing on the deepest point of the crack, and the information about geometric dimension of the nozzle corner is not clear. According to the previous fatigue test results regarding the surface crack at the nozzle corner, the amounts of crack growth at the surface points were larger than that at the deepest point of the crack. Such results imply that SIFs at the surface points may be higher than that at the deepest point. To increase the reliability of the structural integrity assessment, it is necessary to provide SIF solutions for both surface and deepest points. In this study, SIF solutions for two surface points and the deepest point of surface crack at nozzle corners are developed through finite element analyses and the solutions are provided corresponding to the geometric dimensions of nozzle corner and crack size.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Tokiyoshi, Masanori*; Nishiyama, Kyohei*; Sato, Rina; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Funaki, Hironori; Abe, Tomohisa; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Nagamine, Haruo*; Fujisaka, Motoyuki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(2), p.87 - 96, 2023/04
Since the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, many decontamination works have been carried out, but it is difficult to say that much data on workers' exposure has necessarily been analyzed in detail. In this paper, based on the GPS location information carried by the workers together with their personal dosimeters, the air dose rate in the work area and the characteristics of each type of work were analyzed. The results showed that more than 50% of the measured actual doses were more than twice the median planned dose calculated from the air dose rate and actual working hours. Furthermore, as a result of the analysis by work type, it was found that the exposure doses of demolition workers tended to be high, and that this was due to the fact that most of the work was carried out before the work was carried out to reduce the dose at the work site. In addition, when the conversion from air dose to effective dose was taken into account, there were many cases of underestimation where the planned values were lower than the measured values, and it is considered important for management to set appropriate working factor.
 , ThO
, ThO , UO
, UO , PuO
, PuO , and (U, Pu)O
, and (U, Pu)O
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1081473_1 - 1081473_10, 2023/01
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(4), p.041503_1 - 041503_12, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:29.26(Environmental Sciences)Sheltering is one of the countermeasures against radiation exposure during nuclear accidents. The effectiveness of sheltering for inhalation exposure is often expressed by the reduction factor, which is defined as the ratio of the indoor to the outdoor cumulative radioactivity concentrations or doses. The indoor concentration is mainly controlled by the air exchange rate, penetration factor, and indoor deposition rate. Meanwhile, the air exchange rate depends on surrounding environmental conditions: the wind speed, leakage area normalized by the floor area of the house, and gross building coverage ratio. In this study, the ranges of the uncertainty of the reduction factors for particles and I were investigated under various environmental conditions, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to understand the parameter with the most influence on the uncertainty of the reduction factor. From the results of the uncertainty analyses, the calculated reduction factor was highly variable depending on the environmental condition and the airtightness of the houses. The uncertainty ranges of the reduction factor for particles and I
were investigated under various environmental conditions, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to understand the parameter with the most influence on the uncertainty of the reduction factor. From the results of the uncertainty analyses, the calculated reduction factor was highly variable depending on the environmental condition and the airtightness of the houses. The uncertainty ranges of the reduction factor for particles and I were up to 0.9 and 0.3, respectively, and were smaller for newer houses. From the results of the sensitivity analyses, the wind speed was the most influential parameter on the reduction factor. Additionally, the wind speed was less influential for the reduction factor in newer houses.
were up to 0.9 and 0.3, respectively, and were smaller for newer houses. From the results of the sensitivity analyses, the wind speed was the most influential parameter on the reduction factor. Additionally, the wind speed was less influential for the reduction factor in newer houses.
Kam, D. H.*; Grabaskas, D.*; Starkus, T.*; Bucknor, M.*; Uchibori, Akihiro
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 126(1), p.536 - 539, 2022/06
Removal of gaseous radionuclides from the bubbles released into the sodium pool is an important consideration of fuel pin failure accident in sodium-cooled fast reactors. To support modeling of this phenomenon as a part of development of the SRT (Simplified Radionuclide Transport) code in Argonne National Laboratory, numerical analysis of experiment on Iodine gas transport to sodium pool was performed. A proposed evaluation method can be regarded to be reasonably predicting the measured decontamination factors.
Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru; Takahashi, Fumiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.656 - 664, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is known that internal doses depend on the physical characteristics of an evaluation subject. Internal dose coefficients provided by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) are evaluated using the characteristics of the standard Caucasian. It is important to grasp the variations of doses due to the differences in characteristics between Japanese and Caucasian when the dose coefficients of ICRP are applied to Japanese. This study evaluated dose coefficients using specific absorbed fraction (SAF) data based on the average adult Japanese physique which was developed by modification of the existing Japanese SAF data with additional calculations to make the existing data fit to the current dosimetric methodology of ICRP and compared them to those provided by ICRP. As a result, the discrepancies in dose coefficients were smaller than plus or minus 10% in most intake conditions. However, some intake conditions indicated varieties over 40% due to the differences in organ masses, amount of adipose tissues around the thoracic cavity, and so on. This information is useful in application of ICRP's dose coefficients to population of which physical characteristics are different from those of Caucasian. Further, the Japanese SAF data is published as an appendix of this paper.
Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kato, Masaji*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Kono, Masanori*; Sato, Toshinori
Journal of MMIJ, 138(4), p.44 - 50, 2022/04
It is important to understand the long-term migration of radionuclides when considering rock engineering projects such as the geological disposal of radioactive waste. The network of fractures and pores in a rock mass plays a major role in fluid migration as it provides a pathway for fluid flow. The geometry of a network can change due to fracture sealing by some fine-grained materials over long-term periods. In the present study, we use a macro-fractured granite sample to investigate the change of permeability that occurs under the flow of water that includes two different amounts of clay. Findings showed that clay accumulated in a fracture and that the permeability (hydraulic conductivity) of the granite sample decreased over time, which was greater in for the higher clay content. We concluded that the accumulation of clay minerals in the fracture decreased the permeability of the rock. Furthermore, we consider that the filling and closure of fractures in rock is possible under the flow of groundwater that includes clay minerals.

Watanabe, Masashi; Seki, Takayuki*
Materials Science & Engineering B, 272, p.115369_1 - 115369_6, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effect of oxygen non-stoichiometry on the initial sintering behavior of CeO was investigated. It was found that the initial sintering of the stoichiometric and hypo-stoichiometric composition was controlled by the grain boundary diffusion. The activation energies of cation diffusion were derived from initial sintering data. Moreover, it is suggested that the cation diffusion was caused by a vacancy mechanism.
was investigated. It was found that the initial sintering of the stoichiometric and hypo-stoichiometric composition was controlled by the grain boundary diffusion. The activation energies of cation diffusion were derived from initial sintering data. Moreover, it is suggested that the cation diffusion was caused by a vacancy mechanism.
Sun, Haomin; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hirose, Yoshiyasu; Kukita, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(9), p.1048 - 1057, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:55.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Atsushi; Kibe, Satoshi*; Kawanobe, Kazunori*; Fujisaku, Kazuhiko*; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Suzuki, Hideya*; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsumura, Tatsuro
JAEA-Research 2021-003, 30 Pages, 2021/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing a solvent extraction process called SELECT to recover minor actinides (MA) from spent nuclear fuel. In the SELECT process, TDdDGA, HONTA, and ADAAM are used as the extractants for MA + Ln corecovery, MA/Ln separation and Am/Cm separation, respectively. These extractants do not contain phosphorus (P), and consist of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N). In this study, in order to give beneficial information for designing flowsheet, the mass transfer coefficients of Ln between HNO solution and TDdDGA or HONTA / n-dodecane solvent were evaluated by the single drop technique. Prior to the evaluation of mass transfer coefficient, we had optimized the structure of the single drop apparatus to improve accuracy of the measurement. Based on the mass transfer coefficients obtained in HNO
solution and TDdDGA or HONTA / n-dodecane solvent were evaluated by the single drop technique. Prior to the evaluation of mass transfer coefficient, we had optimized the structure of the single drop apparatus to improve accuracy of the measurement. Based on the mass transfer coefficients obtained in HNO / TDdDGA-n-dodecane system, Ln behaviors in the counter-current extraction and back-extraction using mixer-settlers and centrifugal contactors were estimated by simple calculation, and they had a good agreement with our previous experimental results. We also confirmed the mass transfer coefficients of Ln in HNO
/ TDdDGA-n-dodecane system, Ln behaviors in the counter-current extraction and back-extraction using mixer-settlers and centrifugal contactors were estimated by simple calculation, and they had a good agreement with our previous experimental results. We also confirmed the mass transfer coefficients of Ln in HNO / HONTA - n-dodecane system are under 10
/ HONTA - n-dodecane system are under 10 m/s.
m/s.
 Cs to web-building spiders,
Cs to web-building spiders,  , and its pathways; A Preliminary study using stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analyses
, and its pathways; A Preliminary study using stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analysesTanaka, Sota; Kakinuma, Hotaru*; Adachi, Taro*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.507 - 514, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Understanding the pathways of  Cs transfer to predatory spiders is useful to assess long-term behavior of
Cs transfer to predatory spiders is useful to assess long-term behavior of  Cs in the environment, because spiders obtain food resources from both the grazing and detritus food chains in terrestrial-aquatic linking forest ecosystems. In the present study, we collected spider samples at forest interior and riverside. The sample collection was approximately 6.5 years after the FDNPP accident. Moreover, a transfer factor value (T
Cs in the environment, because spiders obtain food resources from both the grazing and detritus food chains in terrestrial-aquatic linking forest ecosystems. In the present study, we collected spider samples at forest interior and riverside. The sample collection was approximately 6.5 years after the FDNPP accident. Moreover, a transfer factor value (T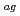 ) for
) for  Cs in spiders was quantified. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios (
Cs in spiders was quantified. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios (
 C and
C and 
 N) of the spiders were also investigated to estimate the transfer pathways of
N) of the spiders were also investigated to estimate the transfer pathways of  Cs to the spiders.
Cs to the spiders.
Hirouchi, Jun; Tokashiki, Yuji*; Takahara, Shogo; Manabe, Kentaro
JAEA-Research 2021-001, 284 Pages, 2021/03
Doses to the public are calculated with internal dose coefficients based on the publications of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in OSCAAR, which is a level 3 Probabilistic Risk Assessment code developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The gastrointestinal absorption fraction, 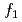 , which is one of parameters of internal dose coefficient, is given the recommended value. However, although it has been reported that
, which is one of parameters of internal dose coefficient, is given the recommended value. However, although it has been reported that 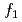 has uncertainty, the uncertainty analysis of
has uncertainty, the uncertainty analysis of 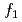 has been performed on few radionuclides. In this report, to evaluate the influence of uncertainty of
has been performed on few radionuclides. In this report, to evaluate the influence of uncertainty of 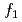 on the internal dose, we calculated the internal dose coefficient with various
on the internal dose, we calculated the internal dose coefficient with various 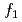 , and derive the relationship between the coefficient and
, and derive the relationship between the coefficient and 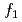 . As a result, we indicate that the relationships are expressed by a linear function for radionuclides with a half-life of more than 0.5 days and are expressed by a cubic function for radionuclides with a half-life of less than 0.5 days.
. As a result, we indicate that the relationships are expressed by a linear function for radionuclides with a half-life of more than 0.5 days and are expressed by a cubic function for radionuclides with a half-life of less than 0.5 days.
Tsutsui, Nao; Ban, Yasutoshi; Suzuki, Hideya*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Ito, Sayumi*; Inaba, Yusuke*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Takeshita, Kenji*
Analytical Sciences, 36(2), p.241 - 246, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:81.93(Chemistry, Analytical)To investigate the effective separation of actinides (Ans) from lanthanides (Lns), single-stage batch extraction experiments were performed with a novel extractant, tetradodecyl-1,10-phenanthroline-2,9-diamide (TDdPTDA) with various diluents such as 3-nitrobenzotrifluoride (F-3), nitrobenzene, and  -dodecane for Am, Cm, and Lns. The extraction kinetics with TDdPTDA was rapid enough to perform the actual extraction flow sheet. The slopes of the distribution ratio versus TDdPTDA concentration and the distribution ratio versus nitric acid concentration were similar for F-3 and nitrobenzene systems but different from
-dodecane for Am, Cm, and Lns. The extraction kinetics with TDdPTDA was rapid enough to perform the actual extraction flow sheet. The slopes of the distribution ratio versus TDdPTDA concentration and the distribution ratio versus nitric acid concentration were similar for F-3 and nitrobenzene systems but different from  -dodecane system. These differences were attributed to the characteristics of the diluents. This study reveals high distribution ratios of Am (
-dodecane system. These differences were attributed to the characteristics of the diluents. This study reveals high distribution ratios of Am (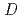
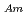 ) and Cm (
) and Cm (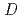
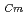 ) for TDdPTDA, with the high separation factors (
) for TDdPTDA, with the high separation factors ( s) of Am from Lns enough for their separation.
s) of Am from Lns enough for their separation.
Mihara, Morihiro; Harasawa, Shuichi*; Torii, Kazuyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 26(1), p.15 - 23, 2019/06
Hardened cement pastes (HCPs) of water/cement ratio (W/C) 50% and 30% using fly ash (FA), blast furnace slag (BFS) and silica fume (SF) for 28 days were prepared. Apparent diffusion coefficients (D ) of Cs and I in HCPs were obtained using electron probe microanalysis. For Cs, BFS and SF contributed to a reduction of D
) of Cs and I in HCPs were obtained using electron probe microanalysis. For Cs, BFS and SF contributed to a reduction of D for W/C=50% and 30%, respectively. For I, BFS reduced D
for W/C=50% and 30%, respectively. For I, BFS reduced D for W/C=50%, however a significant reduction in D
for W/C=50%, however a significant reduction in D for W/C=30% was not observed. Using SF enhanced sorption of Cs on HCP, and using BFS slightly improved sorption of Cs on HCP. It was also confirmed that the pore structures of HCP using SF and BFS were connected by fine pores. It was therefore considered that using SF and BFS contributes to the reduction of D
for W/C=30% was not observed. Using SF enhanced sorption of Cs on HCP, and using BFS slightly improved sorption of Cs on HCP. It was also confirmed that the pore structures of HCP using SF and BFS were connected by fine pores. It was therefore considered that using SF and BFS contributes to the reduction of D in HCP.
in HCP.
Sun, Haomin; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Okagaki, Yuria; Yonomoto, Taisuke
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2019, p.1743982_1 - 1743982_15, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru; Takahashi, Fumiaki
BIO Web of Conferences (Internet), 14, p.03011_1 - 03011_2, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Public, Environmental & Occupational Health)Dose coefficients, which are committed effective dose per unit intake of radionuclides, are fundamental amounts for dose estimation and protection standards against internal exposures. In this study, we built a calculation function of dose coefficients using the latest dosimetric models and data as a part of development of internal dosimetry code in accordance with 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission of Radiological Protection (ICRP). Quality of the function was assured by comparing the results generated by the function to values recorded in a database of dose coefficients for workers provided by ICRP. In the presentation, we will report the results of quality assurance and the future plans of code development.
Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru; Takahashi, Fumiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(5), p.385 - 393, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)At high energy accelerator facilities, various radionuclides are produced by nuclear reactions of high energy particles with structure and/or ambient air of the facilities. Consequently, the radionuclides are potential sources of internal exposure for works of the facilities. However, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) do not provide dose coefficients, which are committed effective doses per intake, for the short-lived radionuclides whose half-lives are shorter than 10 minutes in accordance with the ICRP 2007 Recommendations. Then, we estimated the dose coefficients for inhalation and ingestion of these short-lived radionuclides in accordance with the ICRP 2007 Recommendations. In addition, we compared the dose coefficients with those in accordance with the ICRP 1990 Recommendations. As a result, a decreasing tendency was shown in the dose coefficients for inhalation cases; an increasing tendency was observed in those for ingestion cases. It was found that these changes in dose coefficients were mainly caused by the revision of the dose calculation procedures, alimentary tract models. The result of this study will be useful for planning of radiation protection at the high energy facilities.
Kubota, Kenji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sugita, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2019 Rock Dynamics Summit in Okinawa (USB Flash Drive), p.729 - 733, 2019/05
During the excavation of shafts and galleries in the deep subsurface for disposing of high-level radioactive waste, an excavation disturbed zone (EdZ) or excavation damaged zone (EDZ) is developed around the shafts and galleries. Such zones could influence the transfer behavior of radioactive nuclides, and it is therefore important to understand the behavior of the EdZ or EDZ. We performed in situ experiments before, during, and after gallery excavation in galleries of 140 and 250 m in depth in an area of soft sedimentary rock in Japan. The results demonstrate that the extent of fractures induced by the gallery excavation related with EDZ was confined to about 0.45 m from the gallery wall in the 140 m gallery and to about 1 m from the gallery wall in the 250 m gallery. The extent of the unsaturated zone related with EdZ was about 1 m in the 140 m gallery, but an unsaturated zone did not appear in the 250 m gallery.
 O in Fe
O in Fe O
O film on Fe formed in an NaOH solution containing oxidants
film on Fe formed in an NaOH solution containing oxidantsHaruna, Takumi*; Miyataki, Yuki*; Hirohata, Yohei*; Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 67(9), p.375 - 380, 2018/09
This research aimed to confirm the formation of Fe O
O film on Fe immersed in aqueous 45 mass% NaOH solution containing some oxidants at the boiling temperature, to recognize the optimum immersion time for the formation of thick and protective film, and to reveal the absorption behavior of D
film on Fe immersed in aqueous 45 mass% NaOH solution containing some oxidants at the boiling temperature, to recognize the optimum immersion time for the formation of thick and protective film, and to reveal the absorption behavior of D O in the Fe
O in the Fe O
O film at room temperature. The results were obtained as follows. It was confirmed that Fe
film at room temperature. The results were obtained as follows. It was confirmed that Fe O
O film was formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for a time more than 0.6 ks, and the film thickness increased parabolically with an increase in the immersion time. D
film was formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for a time more than 0.6 ks, and the film thickness increased parabolically with an increase in the immersion time. D O absorption test was carried out to the films formed in the NaOH solution for immersion times of 1.2 and 3.6 ks. An amount of D
O absorption test was carried out to the films formed in the NaOH solution for immersion times of 1.2 and 3.6 ks. An amount of D O absorbed into the film increased with an increase in an absorption time up to 1000 ks, and an absorption time more than 1000 ks made an amount of D
O absorbed into the film increased with an increase in an absorption time up to 1000 ks, and an absorption time more than 1000 ks made an amount of D O constant. The constant amount of D
O constant. The constant amount of D O was larger for the film formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for 3.6 ks than that for 1.2 ks. The transient of the amount of D
O was larger for the film formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for 3.6 ks than that for 1.2 ks. The transient of the amount of D O absorbed into the film was analyzed on the basis of Fick's law for diffusion, and diffusion coefficients of D
O absorbed into the film was analyzed on the basis of Fick's law for diffusion, and diffusion coefficients of D O were obtained to be 5.1
O were obtained to be 5.1 10
10 cm
cm s
s and 9.9
and 9.9 10
10 cm
cm s
s for the films formed for 1.2 and 3.6 ks, respectively. Therefore it was estimated that the diffusion coefficient of the Fe
for the films formed for 1.2 and 3.6 ks, respectively. Therefore it was estimated that the diffusion coefficient of the Fe O
O film was in the region from 5.1
film was in the region from 5.1 10
10 cm
cm s
s to 9.9
to 9.9 10
10 cm
cm s
s .
.